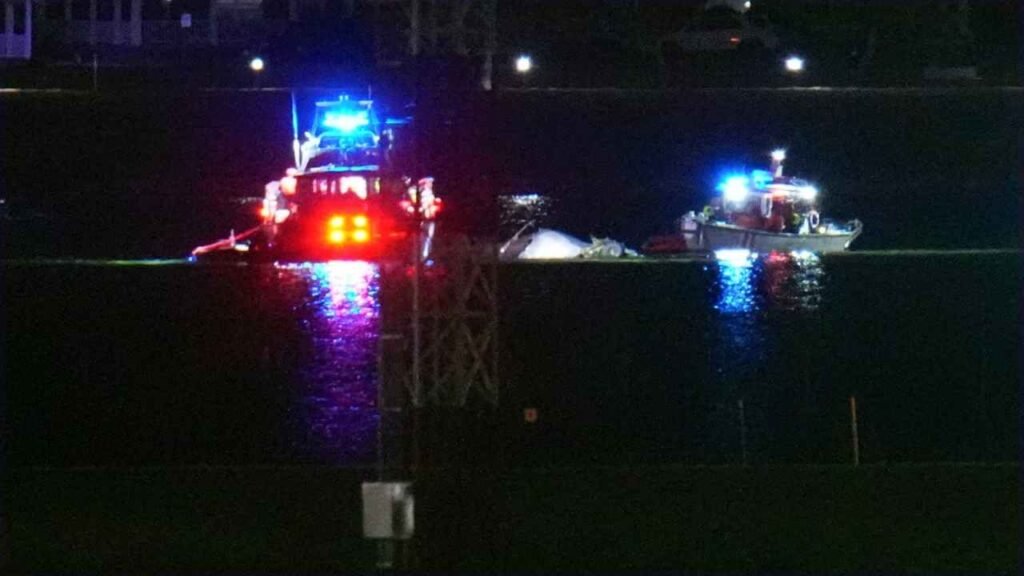
A tragic aviation accident unfolded near Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport when an American Airlines flight collided with a helicopter over the Potomac River in 2025. This mid-air crash resulted in multiple casualties, operational disruptions, and financial setbacks.
The incident has raised concerns about aviation safety, mid-air collision risks, and flight coordination. Airlines Flight and Helicopter Collision, the capabilities of both aircraft, the primary reasons behind the collision, and the financial impact on the airline and helicopter operator.
What Happened in the Airlines Flight and Helicopter Collision?
Details of the Incident
According to initial reports, an American Airlines commercial aircraft was approaching Washington, D.C., when it collided with a private helicopter operating within the same airspace. The impact caused severe damage, leading to the airplane’s descent into the Potomac River.
Immediate Aftermath
- Emergency responders rushed to the scene for rescue operations.
- The FAA (Federal Aviation Administration) and NTSB (National Transportation Safety Board) began an official investigation.
- The collision resulted in multiple fatalities and injuries.
- Air traffic was disrupted, affecting flight schedules at Reagan National Airport.
Capabilities of the American Airlines Aircraft and Helicopter
American Airlines Aircraft Specifications
The aircraft involved in the crash was a Boeing 737, known for its fuel efficiency and reliability in domestic and international flights. Key features include:
- Passenger Capacity: 150–180 passengers.
- Cruise Speed: Approximately 530 mph.
- Navigation System: Advanced TCAS (Traffic Collision Avoidance System).
- Safety Features: Automated alerts for mid-air proximity threats.
Helicopter Specifications
The helicopter involved was a Robinson R44, a commonly used private and commercial rotorcraft. Features include:
- Passenger Capacity: 2–4 passengers.
- Cruise Speed: Around 130 mph.
- Navigation System: GPS-based flight assistance.
- Flight Altitude: Typically 500–10,000 feet.
The significant speed difference and maneuverability between the aircraft likely contributed to the collision risk.
Primary Causes of the American Airlines and Helicopter Collision
1. Air Traffic Control Failure
- Possible miscommunication between air traffic controllers and pilots.
- Failure to assign clear altitude and flight paths.
2. Pilot Error
- The helicopter pilot may have misjudged the aircraft’s approach path.
- Delayed evasive action due to limited visibility.
3. Mechanical or Navigation Failure
- Potential faults in the aircraft’s TCAS system.
- The helicopter may have experienced navigation failure.
4. Poor Weather Conditions
- Reduced visibility due to fog or rain.
- Wind turbulence affecting flight control.
Impact and Losses Due to the Collision
1. Loss of Human Lives and Injuries
- Multiple fatalities and serious injuries.
- Psychological trauma for survivors and families.
2. Financial Cost to American Airlines
- Aircraft loss: Estimated at $100 million for a new Boeing 737.
- Compensation payouts: $2.5–$4 million per victim.
- Legal settlements and lawsuits could cost millions more.
- Operational disruptions: Flight delays, cancellations, and temporary grounding of aircraft.
3. Financial Cost to the Helicopter Operator
- Helicopter damage: Estimated at $500,000–$1 million.
- Loss of pilot and passengers leading to compensation claims.
- Increased insurance costs affecting future operations.

How Mid-Air Collisions Impact Airlines and Helicopter Operators
1. Reputation Damage
- Passenger confidence declines, affecting ticket sales.
- Brand trust takes a hit, requiring aggressive PR campaigns.
2. Increased Insurance Premiums
- Insurance rates can increase by 20–50% for both the airline and the helicopter operator.
- Stricter insurance policy evaluations and deductibles.
3. Regulatory Penalties and Stricter Safety Checks
- FAA and NTSB may impose penalties on American Airlines.
- Helicopter operators may face tighter airspace restrictions.
- Airlines may need additional pilot training programs.
How Can Mid-Air Collisions Be Prevented?
1. Enhanced Air Traffic Control Systems
- Upgraded real-time monitoring and radar systems.
- AI-based automated collision prevention alerts.
2. Mandatory Use of Advanced TCAS in Helicopters
- Helicopters should be required to have collision avoidance technology similar to commercial jets.
3. Improved Pilot Training
- Stricter altitude awareness training for helicopter pilots.
- More simulator-based collision avoidance training.
4. Stricter Airspace Regulations
- Designation of separate flight corridors for helicopters and airplanes.
- Minimum separation distances enforced by authorities.
Conclusion
The American Airlines flight and helicopter collision in Washington is a tragic reminder of the importance of air traffic safety and coordination. The financial losses, reputational damage, and loss of human lives make it imperative for aviation authorities to enhance regulations, improve pilot training, and invest in advanced safety technologies.
As the FAA and NTSB investigation continues, it is crucial to implement lessons learned from this tragedy to prevent future mid-air collisions. Stricter safety measures, improved air traffic control systems, and advanced collision avoidance technology are necessary to